All the photos below are from the patients under the care of Dr. Zhu, all the photos were taken by Dr. Zhu, posted for the purpose of education , all rights reserved.
A cataract is a clouding of the normally clear lens of the eye. Proteins and fibers in the lens break down, causing vision to become hazy. People who have cataracts will experience foggy cloudy blurry vision, more difficult to read, drive a car (especially at night). . They will need stronger lighting and change of eyeglasses Rx. But if the daily activities impaired, cataract surgery is needed.
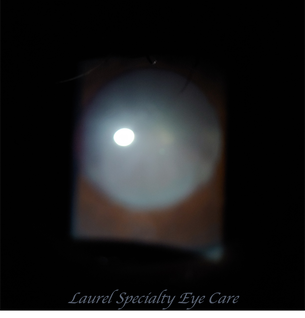
Nuclear Sclerosis Cataract
There are several types of cataracts, The most common cataracts are age related, like Nuclear Sclerosis Cataracts. UV light from the sun and smoke are risk factors.
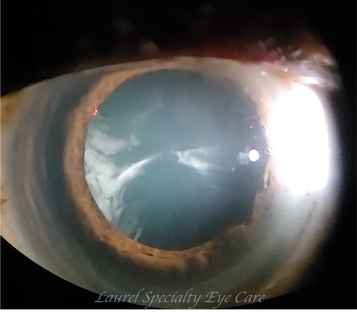
Cortical Cataract
Cortical cataracts develop in the edges of the lens and then make their way towards the center in a spoke-like manner. Age is the primary cause of cortical cataract.
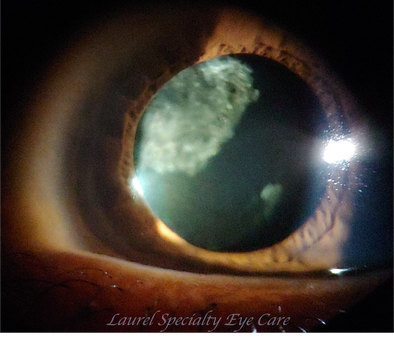
Posterior Subcapsular Cataract (PSC)
Posterior subcapsular cataract (PSC) is a fast-growing opacity in the rear of the natural lens. This cataract is most common in people who take steroids or have diabetes.
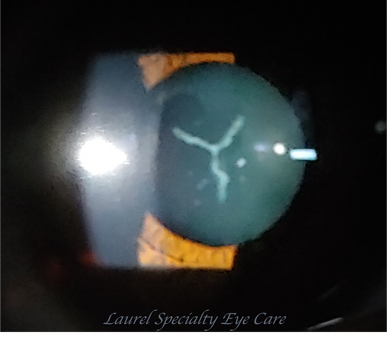
“Y-suture” Cataract
This is a congenital lens opacity that occurs at the location of closure of the fetal lenticular nucleus. These are rarely visually significant. The Y sutures demarcate the boundaries between the lens cortex, which is peripheral to the Y sutures, and the lens nucleus, which is within and includes the Y sutures. The anterior Y suture is oriented upright, and the posterior Y suture is inverted.
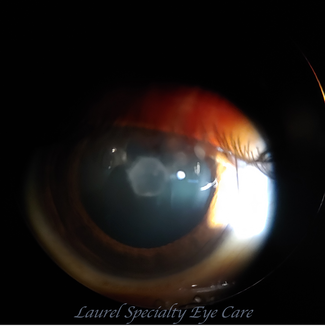
Lamellar or Zonular Cataract
Lamellar or zonular cataract is another type of congenital cataract. The lens opacities are located at the level of the primary fibers in the embryonic nucleus. This cataract is usually bilateral and asymmetrical.
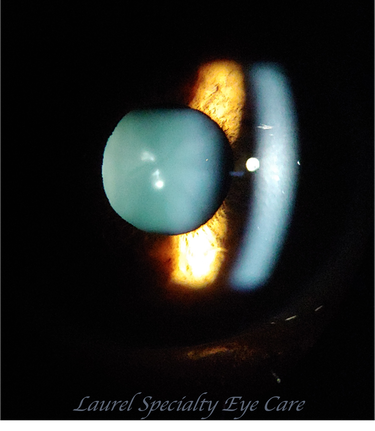
Dot Cataract
This is congenital cataract with dot opacity, usually is not visually significant
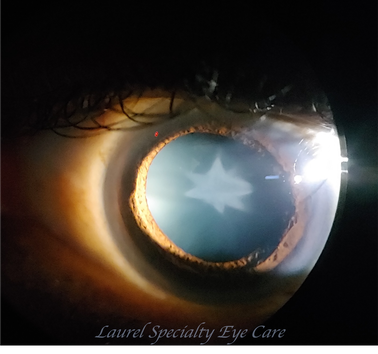
Rosette Cataract
Also called traumatic cataract, caused by blunt trauma to the eye.